250 BC: In On the Sphere and the Cylinder, Archimedes gives the formulae for calculating the volume of a sphere and a cylinder. In Measurement of the Circle he gives an approximation of the value of π with a method which will allow improved approximations. In Floating Bodies he presents what is now called “Archimedes’ principle” and begins the study of hydrostatics. He writes works on two- and three-dimensional geometry, studying circles, spheres and spirals. His ideas are far ahead of his contemporaries and include applications of an early form of integration.
Category: tidbits

Algebra
Around 825 A.D. in Baghdad, Mohammed ibn-Musa al-Khwarizimi wrote a book called “Kitab al-jabr wa al-muqabalah”, which means “The science of restoration and reduction” and stood as the major algebraic work of the period. The word “algebra” comes from this title (“al-jabr”), since this was the first textbook used in Europe for this subject. The word “algorithm” is a distortion of al-Khwarizmi’s name. http://www.factme.com/category10.html
Abacus
The abacus was developed in the Middle East and areas around the Mediterranean in about 3000 BC.

1st Woman Mathematician
In 400 AD, Hypatia writes commentaries on Diophantus and Apollonius. She is the first recorded female mathematician and she distinguishes herself with remarkable scholarship. She becomes head of the Neo-Platonist school at Alexandria.
Raphael even includes Hypatia in his masterpiece Phillosphy, or School of Athens, shown above. This painting features the greatest minds in history up to the time of Raphael.
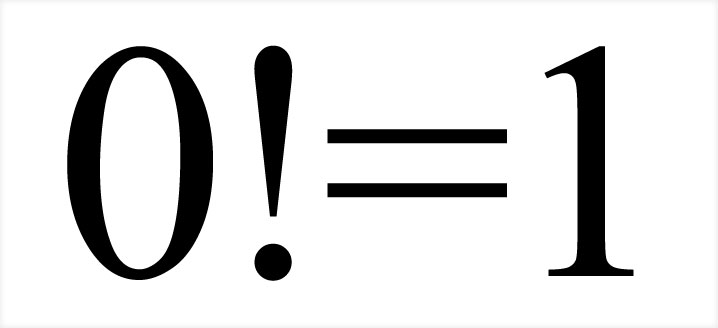
0! = 1
0! = 1 (zero factorial equals one)
.
.
.
5! = 5x4x3x2x1 = 120
4! = 4x3x2x1 = 24
3! = 3x2x1 = 6
2! = 2×1 = 2
1! = 1
0! = 1
